Iraq’s oil and ICT sectors are foundational to national prosperity and security; leveraging AI securely requires alignment with constitutional mandates (Articles 111–112), the National Development Plan 2024–2028 (ICT and energy pillars), and international best practices (NIST RMF, ISO 42001, OECD). This submission document, in Arabic and English side-by-side, integrates: (1) a two-page Executive Summary with strategic alignment and approval pathways; (2) Legal & Policy Foundations anchored in the Constitution and draft Federal Oil Law; (3) a structured Bilingual Format with annexes; (4) a Detailed Budget & Resource Plan linked to roadmap phases; (5) an Enhanced Risk Register with owners; (6) Stakeholder Engagement workflows and sign-off procedures; (7) a Milestone-driven Implementation Roadmap with KPIs; and (8) Appendices including draft decrees and MoU templates.
Executive Summary
- Purpose & Scope: Joint submission to Ministry of Oil and Iraqi Supreme Committee for AI, reflecting mandates under Articles 111–112 of the Constitution (Norton Rose Fulbright).
- Strategic Alignment: Direct linkage to Iraq’s National Development Plan 2024–2028, particularly Objective 3 on telecommunications and informatics, and energy modernization goals (FAOLEX).
- Key Recommendations: Five pillars—Governance, Security, Risk Management, Data Governance, Capacity Building—each with impact statements.
- Approval Pathway: Review and sign-off through:
- Ministry of Oil Strategic Planning Department
- Supreme Committee’s Digital Transformation & Automation Center (Iraq Business News)
- Cabinet-level endorsement
- Legal & Policy Foundations
1.1 Constitutional Mandate
- Article 111: “Oil and gas are owned by all the people of Iraq in all the regions and governorates,” establishing federal stewardship (Norton Rose Fulbright).
- Article 112: Mandates joint management and revenue distribution by federal, regional, and governorate authorities (Norton Rose Fulbright).
- Draft Federal Oil Law: Recites Article 111 and interprets federal authority over oil management, providing legislative context for AI governance within the Ministry’s remit (Stanford Law School).
1.2 National Development Goals
- ICT Pillar: “Keep pace with the rapid development of telecommunications and informatics” to position Iraq as a regional ICT hub (FAOLEX).
- Energy Pillar: INES alignment—to leverage AI for exploration efficiency, grid optimization, and diversification targets.
- Document Format & Accessibility
- Bilingual Presentation: Arabic/English columns throughout to meet Ministry publication standards.
- Structured Annexes:
- Annex A: Glossary of AI and legal terms (bilingual).
- Annex B: Full text of cited constitutional articles and draft laws.
- Annex C: Line-item budget estimates.
- Visual Infographics: One-page dashboards per pillar for executive briefings.
- Detailed Budget & Resource Plan
- Staffing: AI security officers, data stewards, governance secretariat.
- Technology: Licensing for MLOps platforms, adversarial-testing tools, encryption solutions.
- Third-Party Audits: Independent NIST RMF and ISO 42001 compliance reviews.
- Training: UNESCO-backed AI ethics and governance programs for 100 trainers and 500 practitioners (UNESCO).
- Co-funding: Partnership with Digital Cooperation Organization (DCO) for capacity building grants, per PM’s DCO meeting on Nov 25, 2024 (DCO).
- Phased Disbursement: 20 % at pilot approval, 50 % at sectoral rollout, 30 % at nationwide scale.
- Enhanced Risk Register
Risk Category | Description | Mitigation | Owner |
Legal Ambiguity | Uncertainty in Federal vs regional jurisdiction | Embed Articles 111–112; seek formal legal opinion | Legal Affairs, Ministry of Oil |
Data Sovereignty | Cross-border data flows | Local hosting mandates; encrypted enclaves | ICT Authority |
Operational Downtime | AI failures in refineries/telecom networks | Redundancy; automated rollback; 24/7 monitoring | Oil & ICT Operations |
Talent Shortfall | Lack of AI security professionals | UNESCO and DCO fast-track training programs | Supreme Committee for AI |
Each risk entry must receive written sign-off from the identified owner and Supreme Committee.
- Stakeholder Engagement & Governance Sign-Off
- Pre-Submission Workshops: Joint sessions with:
- Ministry of Oil R&D & Strategic Planning
- Supreme Committee’s Digital Transformation Center (DCO)
- Steering Committee Endorsement: Circulate Minutes of Meeting recording scope and budget approval.
- Public Consultation Summary: Attach feedback report from SOMO, NOC, and provincial oil councils.
- Implementation Roadmap with Milestones & KPIs
Phase | Timeline | Milestone | KPI | Review Body |
Phase 1 | Q3–Q4 2025 | Governance structures & policies approved | 100 % of policies ratified | Oil Ministry Steering Committee |
Phase 2 | Q1–Q2 2026 | Pilots in Basra refineries & Baghdad ICT hub | < 5 % incident rate; 80 % system uptime | Supreme Committee for AI |
Phase 3 | Q3–Q4 2026 | Sectoral scale-up across all sites | 90 % KPI attainment | Joint Committee |
Phase 4 | 2027+ | National roll-out & international benchmarking | +10 positions in AI Readiness Index | PMO & Cabinet |
- Appendices & Next Steps
- Appendix D: Draft Ministerial Decree for framework adoption.
- Appendix E: MoU templates with UNESCO and DCO.
- Next Steps:
- Finalize bilingual Executive Summary (5 business days).
- Circulate for legal review (5 days).
- Convene joint sign-off meeting (within 2 weeks).
This submission aligns constitutional, strategic, and international dimensions to ensure Iraq’s oil and ICT sectors adopt AI securely, transparently, and sustainably.
Appendixes
Appendix A: Glossary of Terms (Bilingual: Arabic / English)
A comprehensive glossary defining key terms used throughout the framework, presented in both Arabic and English to ensure clarity and accessibility for all stakeholders.
Example Entries:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) / الذكاء الاصطناعي: The simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems.
- Data Governance / حوكمة البيانات: The overall management of the availability, usability, integrity, and security of data used in an organization.
- Risk Management Framework (RMF) / إطار إدارة المخاطر: A structured approach used to identify, assess, and manage risks.
- ISO 42001 / معيار ISO 42001: An international standard for AI management systems, focusing on the governance of AI technologies.
- Metaverse تقنية الميتافيرس: The metaverse is a loosely defined term referring to virtual worlds in which users represented by avatars interact, usually in 3D and focused on social and economic connection.
Appendix B: Legal Citations and Policy References
A compilation of legal documents and policy references that provide the legal foundation for the framework.
- Iraqi Constitution (2005):
- Article 111: States that oil and gas are owned by all the people of Iraq in all the regions and governorates.
- Article 112: Mandates the federal government, with the producing governorates and regional governments, to manage oil and gas extracted from present fields.
- Draft Federal Oil and Gas Law: Provides a legal framework for the management and development of oil and gas resources.
- National Development Plan 2024–2028: Outlines Iraq’s strategic objectives, including the integration of AI in various sectors.
- Digital Transformation and Automation Center Initiatives: Policies promoting the adoption of digital technologies across government sectors.
- International Standards:
- NIST Risk Management Framework: Provides guidelines for managing cybersecurity risks.
- ISO 42001: Standards for AI management systems.(daw-alfada.com)
Appendix C: Budget Breakdown and Cost Estimates
A detailed financial plan outlining the estimated costs associated with implementing the framework.
- Personnel:
- AI Security Officers: $X million
- Data Stewards: $Y million
- Technology Acquisition:
- AI Platforms and Tools: $Z million
- Training and Capacity Building:
- Workshops and Seminars: $A million
- Certification Programs: $B million
- Infrastructure Development:
- Data Centers: $C million
- Network Upgrades: $D million
- Contingency Funds: $E million
- Total Estimated Budget: $Total million(The New Region)
Note: These figures are illustrative. Detailed financial planning should be conducted to determine accurate estimates.(daw-alfada.com)
Appendix D: Draft Ministerial Decree Templates
Templates for official decrees to be issued by the Ministry of Oil and the Iraqi Supreme Committee for AI to formalize the adoption and implementation of the framework.
- Decree Title: “Adoption of the Iraqi National Framework for Secure Artificial Intelligence in the Oil and ICT Sectors”
- Purpose: To mandate the integration of AI technologies in the oil and ICT sectors in alignment with national strategies.
- Scope: Applies to all governmental and affiliated entities within the oil and ICT sectors.
- Implementation Timeline: Outlined in phases with specific milestones.
- Oversight and Evaluation: Establishment of a monitoring committee to oversee implementation and assess progress.
Appendix E: Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs) Templates
Templates for MoUs to be signed with international partners to facilitate collaboration, knowledge exchange, and support in implementing the framework.
- MoU with UNESCO:
- Objective: Collaboration on AI ethics training and capacity building.
- Scope: Joint development of training materials, workshops, and certification programs.
- MoU with Digital Cooperation Organization (DCO):
- Objective: Technical assistance and funding support for AI initiatives.
- Scope: Provision of expertise, resources, and financial support for pilot projects and scaling efforts.
- MoU with International AI Research Institutes:
- Objective: Research collaboration and technology transfer.
- Scope: Joint research projects, exchange programs, and sharing of best practices.
Appendix F: Stakeholder Engagement and Consultation Summary
A report summarizing the engagement activities conducted with various stakeholders during the development of the framework.
- Workshops Conducted:
- Dates, locations, and participant lists.
- Feedback Received:
- Key insights, concerns, and suggestions from stakeholders.
- Incorporation of Feedback:
- How stakeholder input was integrated into the final framework.
- Future Engagement Plans:
- Ongoing communication strategies and feedback mechanisms.
Appendix G: Risk Register and Mitigation Strategies
A comprehensive risk register identifying potential risks associated with the implementation of the framework and proposed mitigation strategies.
Risk | Description | Impact | Likelihood | Mitigation Strategy |
Legal Ambiguity | Uncertainty in AI-related regulations. | High | Medium | Engage legal experts to clarify and draft necessary regulations. |
Data Privacy Concerns | Potential breaches of sensitive data. | High | High | Implement robust data protection measures and compliance with international standards. |
Resistance to Change | Stakeholder reluctance to adopt new technologies. | Medium | High | Conduct awareness campaigns and provide training programs. |
Technical Challenges | Integration issues with existing systems. | High | Medium | Develop phased implementation plans and provide technical support. |
Appendix H: Implementation Roadmap and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
A detailed roadmap outlining the phases of implementation along with associated KPIs to measure progress and success.
- Phase 1: Planning and Preparation
- Timeline: Q1–Q2 2025
- KPIs: Completion of stakeholder consultations, finalization of legal frameworks.
- Phase 2: Pilot Implementation
- Timeline: Q3–Q4 2025
- KPIs: Successful deployment of pilot projects in selected sites, initial training sessions conducted.
- Phase 3: Scaling and Expansion
- Timeline: Q1–Q2 2026
- KPIs: Expansion of AI applications across additional sites, increased number of trained personnel.
- Phase 4: Evaluation and Optimization
- Timeline: Q3–Q4 2026
- KPIs: Assessment reports completed, refinement of strategies based on feedback.
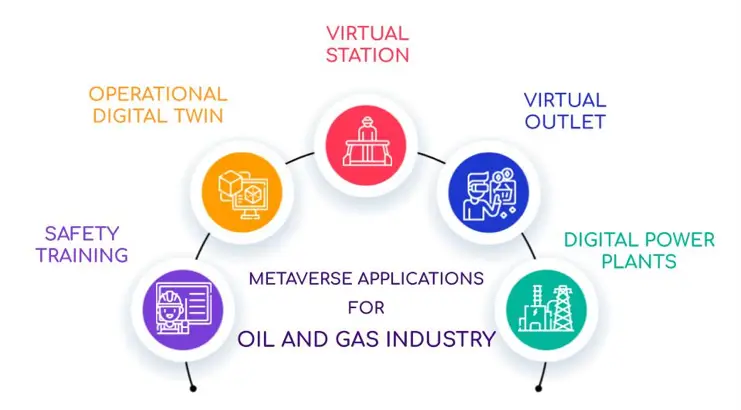
Appendix I: The Metaverse Technology
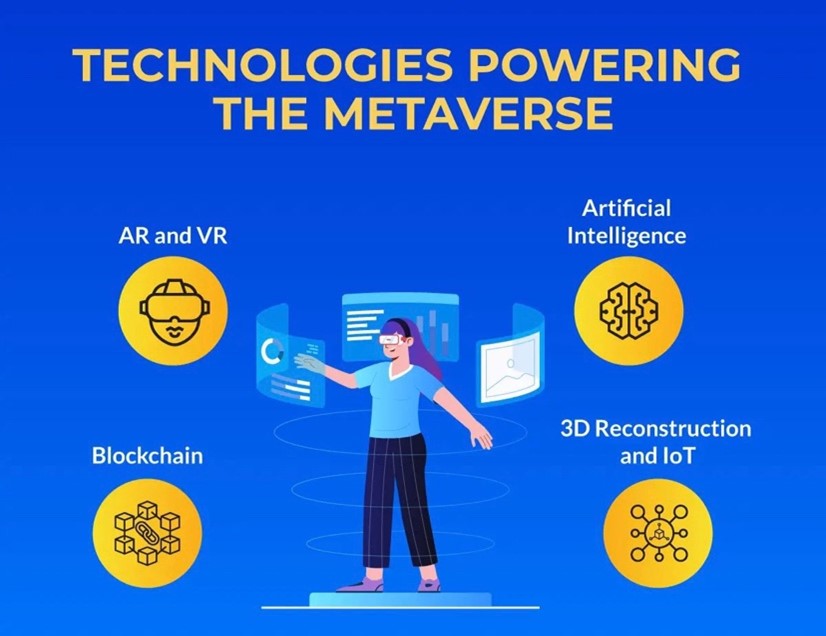
The 4 powers of the metaverse
- Artificial Intelligence
- AR and VR
- 3D reconstruction and IOT
- Blockchain
Can add quality and development powers to the oil sector
Advantages to Iraq Oil sector
Metaverse technologies, including virtual and augmented reality, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT), can potentially increase oil production in Iraq in several ways:
- Remote monitoring and control: IoT sensors and virtual reality can enable remote monitoring and control of oil fields, pipelines, and equipment, improving efficiency and reducing downtime.
- Predictive maintenance: Advanced analytics and machine learning can predict equipment failures, allowing for proactive maintenance and minimizing production disruptions.
- Enhanced collaboration: Virtual reality platforms can facilitate collaboration among teams, enabling experts to share knowledge and expertise remotely, improving decision-making.
- Training and simulation: Virtual reality training simulations can enhance worker skills, reducing errors and improving safety in complex oil production operations.
- Digital twin technology: Creating virtual replicas of oil fields and equipment can optimize production processes, simulate scenarios, and test new strategies without disrupting actual operations.
- Improved supply chain management: Blockchain technology can enhance supply chain transparency, tracking, and management, reducing costs and improving logistics.
- Data-driven decision-making: Advanced data analytics can provide insights into oil reservoir performance, enabling data-driven decisions to optimize production and maximize recovery.
These appendices are designed to provide comprehensive support for the successful adoption and implementation of AI technologies in Iraq’s oil and ICT sectors, ensuring alignment with national objectives and international best practices.