White paper
Dr. Mustafa S. Aljumaily
Research and Development (R&D) Department – Daw Alfada Company
Abstract: The global oil and gas industry is rapidly embracing digital transformation to enhance operational efficiency, safety, and profitability. For Iraqi oil companies, adopting digital technologies is imperative to remain competitive and harness the full potential of their vast natural resources. This white paper provides a comprehensive roadmap for digital transformation in the Iraqi oil industry as of 2025, addressing current challenges, technological enablers, strategic implementation phases, regulatory considerations, and global best practices. By following this roadmap, Iraqi oil companies can position themselves at the forefront of the industry’s digital evolution.
- Introduction
- Overview of Digital Transformation in the Oil Industry: The oil and gas sector is undergoing a paradigm shift with the integration of digital technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and Big Data analytics. These advancements lead to faster, more cost-effective operations, enabling companies to explore previously inaccessible areas and optimize production processes.
- Importance for Iraqi Oil Companies: Iraq, possessing vast oil reserves, has the potential to significantly boost its economy through the oil sector. However, challenges such as deteriorating infrastructure, political instability, and complex regulations hinder progress. Embracing digital transformation can address these issues by improving operational efficiency, ensuring safety, and enhancing decision-making processes.
- Objectives and Scope: This white paper aims to outline a strategic roadmap for Iraqi oil companies to implement digital transformation initiatives effectively. It encompasses an analysis of current challenges, identification of key enabling technologies, phased implementation strategies, regulatory considerations, and insights from global best practices.
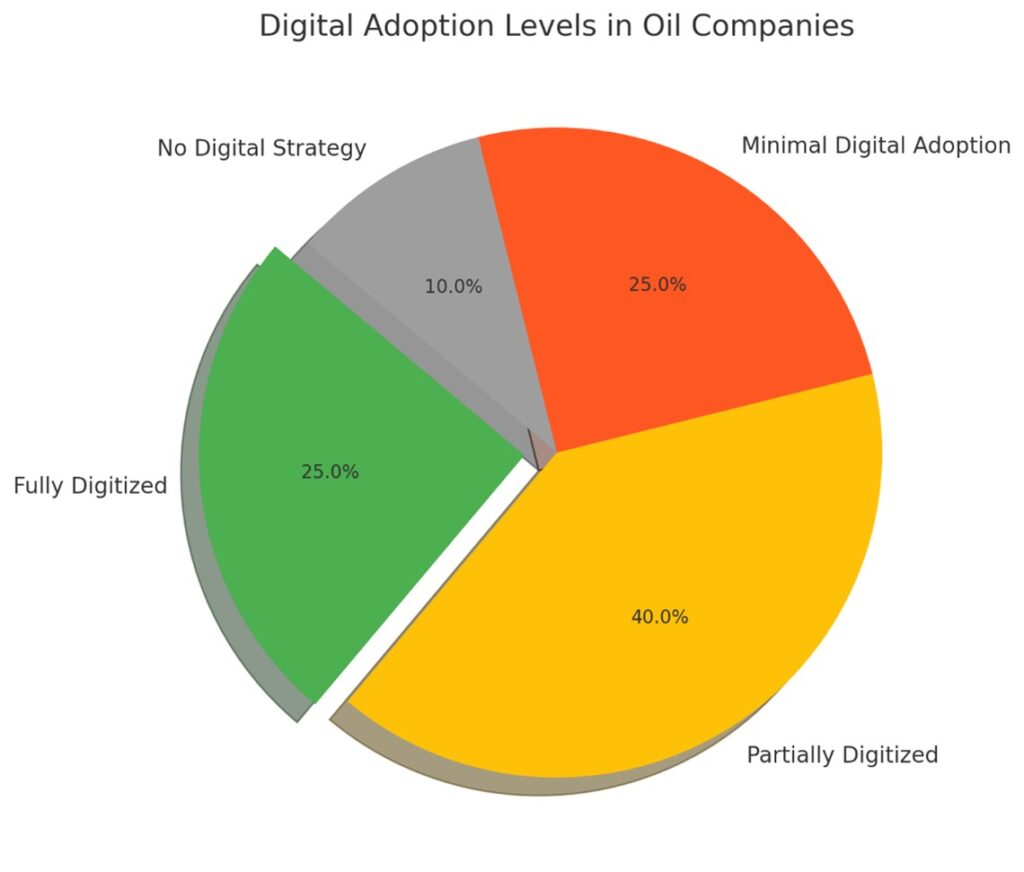
2. Current Challenges in Iraqi Oil Companies
- Legacy Systems and Outdated Infrastructure: Many Iraqi oil companies operate on legacy systems that are inefficient and incompatible with modern digital solutions, leading to operational inefficiencies.
- Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities and Data Management Issues: The lack of coherent information security policies exposes companies to cyber threats, compromising sensitive data and operational integrity.
- Lack of Skilled Workforce in Emerging Technologies: There is a significant gap in the workforce’s digital competencies, hindering the adoption and effective utilization of new technologies.
- Regulatory and Compliance Barriers: Complex and evolving regulations pose challenges in implementing standardized digital solutions, leading to compliance risks.
- Resistance to Change within Organizational Culture: A traditional mindset and resistance to change impede the adoption of innovative digital practices, affecting overall transformation efforts.
-
- Key Technologies Enabling Digital Transformation
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI facilitates predictive maintenance, process optimization, and automated decision-making, leading to increased efficiency and reduced operational costs.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices enable real-time monitoring of pipelines, machinery, and environmental conditions, enhancing safety and operational efficiency.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud platforms provide secure, scalable infrastructure for data storage and analytics, enabling seamless collaboration and data accessibility.
- Big Data and Analytics: Advanced analytics transform vast amounts of data into actionable insights, improving decision-making and operational performance.
- Cybersecurity Solutions: Robust cybersecurity measures protect critical assets from cyber threats, ensuring data integrity and operational continuity.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology enhances transparency in transactions and supply chain management, reducing fraud and improving trust among stakeholders.
- Strategic Roadmap for Digital Transformation
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning
- Conducting a digital maturity assessment.
- Identifying key stakeholders and forming a digital transformation committee.
- Aligning digital initiatives with business objectives.
Phase 2: Infrastructure Modernization
- Upgrading IT infrastructure to support cloud and edge computing.
- Implementing enterprise-wide cybersecurity frameworks.
- Ensuring regulatory compliance with digital policies.
Phase 3: Implementation of Digital Solutions
- Deploying AI-driven analytics for operational efficiency.
- Integrating IoT devices for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
- Transitioning to cloud-based solutions for data storage and collaboration.
Phase 4: Workforce Upskilling and Change Management
- Conducting training programs for employees on digital tools and cybersecurity.
- Encouraging a culture of innovation and digital adoption.
- Developing a governance framework for continuous improvement.
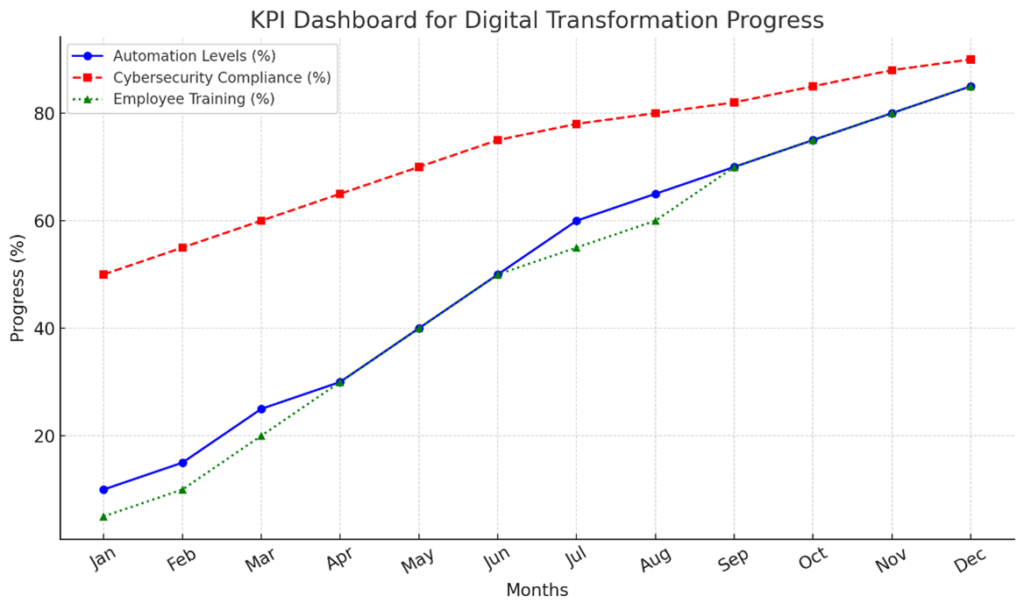
Phase 5: Performance Monitoring and Optimization
- Establishing KPIs to measure digital transformation success.
- Continuous evaluation and refinement of digital strategies.
- Scaling successful initiatives across the organization.
- Considerations for Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
- Overview of Iraqi Regulations Related to Digital Transformation: Iraq is actively advancing its digital transformation through several regulatory initiatives. The introduction of the Digital Payment Regulation No.2 of 2024 aims to reduce reliance on cash, promoting financial inclusion and aligning with global standards. In February 2025, the government launched the Digital Transformation and Automation Center, underscoring a commitment to integrating digital technologies across public services. Additionally, the Central Bank of Iraq plans to issue a national digital currency, gradually replacing paper notes to modernize the financial system. Understanding these evolving regulations is crucial for compliance and to capitalize on emerging opportunities in Iraq’s digital economy.
- International Best Practices for Cybersecurity and Data Protection: Adopting global standards such as ISO 27001 and NIST frameworks enhances data security and operational resilience.
- Compliance with Industry Standards: Ensuring adherence to industry-specific regulations and safety protocols to maintain operational integrity.
- Case Studies and Global Best Practices
- Digital Transformation Success Stories from Leading Oil Companies: Leading oil companies have effectively harnessed digital technologies to enhance operational efficiency. Shell’s Smart Fields initiative integrates real-time data analytics and automation to optimize production and reduce downtime. BP has entered a five-year agreement with Palantir to utilize artificial intelligence for enhancing decision-making processes of its engineers, deploying large language models to analyze data from various operational sites and generate actionable advice. ExxonMobil has adopted advanced technologies to enhance operational efficiency and safety. These cases illustrate the pivotal role of digital transformation in modernizing oil and gas operations.
- Lessons Learned and Key Takeaways for Iraqi Oil Firms: Global oil companies have encountered both successes and challenges in their digital transformation efforts, offering valuable lessons for Iraqi oil firms. A recent survey by Ernst & Young LLP revealed that while 92% of energy companies recognize reskilling as a competitive advantage, only 29% actively invest in retraining, relying instead on on-the-job training, which may delay progress. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) has led to significant efficiency gains; for instance, BP utilizes AI to manage drilling operations, enabling the exploration of previously inaccessible areas. However, challenges persist, such as modernizing legacy systems and managing market volatility. Implementing flexible strategies that align with evolving market trends is crucial. By addressing these factors—workforce development, technology adoption, and strategic flexibility—Iraqi oil firms can enhance their digital transformation initiatives.
- Challenges:
Here is a comparative table outlining the differences between legacy and modern infrastructure in the oil industry:
Category
Legacy Infrastructure
Modern Infrastructure
Technology
On-premise, outdated hardware, limited automation
Cloud-based, AI-driven, IoT-enabled systems
Data Management
Manual record-keeping, isolated databases
Integrated, real-time data analytics and predictive insights
Operational Efficiency
High downtime, reactive maintenance
Predictive maintenance, optimized asset utilization
Security
Vulnerable to cyber threats, weak encryption
Advanced cybersecurity frameworks, AI-driven threat detection
Scalability
Rigid, difficult to expand
Scalable, flexible infrastructure using cloud solutions
Connectivity
Limited remote access, siloed communication
Seamless remote monitoring, cloud-based collaboration
Cost Efficiency
High maintenance costs, inefficient resource allocation
Reduced operational costs, optimized resource usage
Compliance & Regulations
Manual compliance tracking, risk of non-compliance
Automated compliance reporting, adherence to global standards
This table highlights how modern infrastructure significantly enhances efficiency, security, and scalability compared to traditional legacy systems.
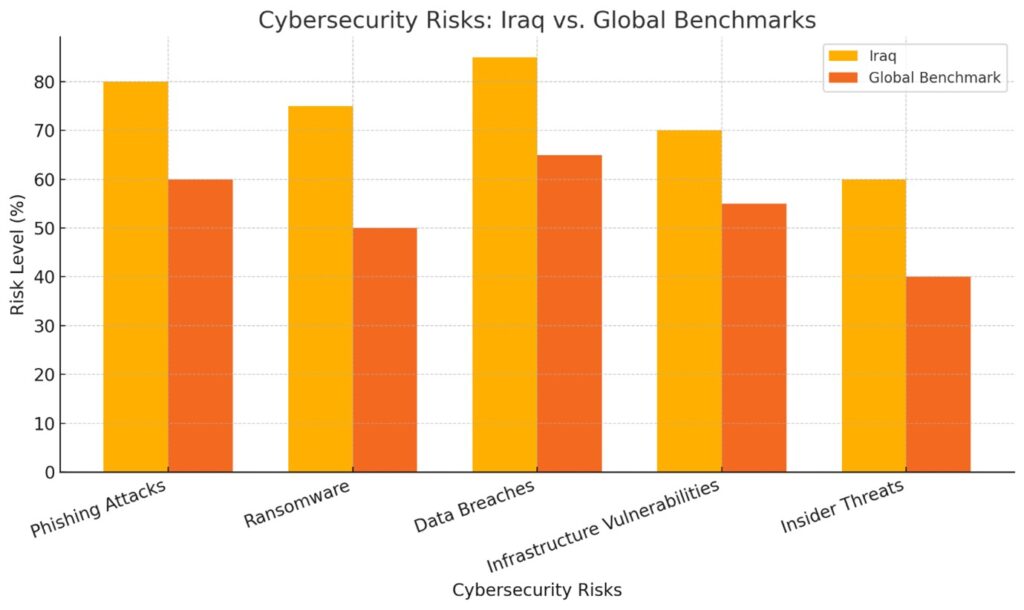
Here is a comparative table highlighting the workforce skills gap in Iraqi oil companies, contrasting current skill levels with the skills required for digital transformation:
Workforce Skills Gap in Iraqi Oil Companies
|
Skill Category |
Current Skill Level (Legacy Workforce) |
Required Skill Level (Digital Transformation Era) |
Gap & Challenges |
|
AI & Data Analytics |
Basic data entry, limited analytics knowledge |
Advanced analytics, AI/ML model development |
Lack of AI expertise, need for upskilling programs |
|
Cloud Computing |
Experience with on-premise servers |
Proficiency in cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) |
Low familiarity with cloud infrastructure |
|
IoT & Automation |
Manual monitoring of equipment and pipelines |
Knowledge of IoT sensors, automated control systems |
Resistance to automation, lack of technical training |
|
Cybersecurity |
Basic IT security measures |
Advanced cybersecurity skills (zero-trust, threat detection) |
High cybersecurity risks due to lack of trained professionals |
|
Software Development & Integration |
Limited coding and system integration experience |
Ability to integrate ERP, SCADA, and AI-driven platforms |
Shortage of software developers with oil & gas expertise |
|
Remote Operations & Digital Tools |
Traditional field-based operations |
Proficiency in digital twin technology, remote asset monitoring |
Hesitancy in adopting digital tools |
|
Compliance & Regulatory Tech |
Manual compliance tracking |
Knowledge of digital compliance systems, automated reporting |
Need for training in regulatory technology |
|
Change Management & Digital Culture |
Resistant to change, traditional workflows |
Adaptive mindset, innovation-driven approach |
Cultural resistance to digital transformation |
This table illustrates the skills gap that Iraqi oil firms must address to successfully implement digital transformation. Bridging this gap requires targeted training programs, industry collaboration, and investment in workforce development initiatives.
Here is a comparative table outlining key regulatory aspects of digital transformation in Iraqi oil companies versus global standards:
Comparison of Iraqi vs. Global Digital Transformation Standards in the Oil Industry
|
Regulatory Area |
Iraqi Regulations |
Global Standards (Best Practices) |
Key Gaps & Challenges |
|
Cybersecurity |
Limited national cybersecurity framework for oil & gas |
NIST, ISO 27001, IEC 62443 (industrial cybersecurity) |
Lack of structured cybersecurity policies and enforcement |
|
Data Protection & Privacy |
No comprehensive data protection law (basic IT security rules exist) |
GDPR (EU), CCPA (US), ISO 27701 (privacy framework) |
Weak data governance policies, lack of compliance mechanisms |
|
Digital Infrastructure Standards |
No clear national guidelines for cloud & AI adoption |
Cloud Security Alliance (CSA), IEEE AI Ethics Guidelines |
Absence of formal cloud & AI regulations for oil sector |
|
Automation & AI Regulation |
No AI governance framework for industrial automation |
EU AI Act, US NIST AI Risk Management Framework |
No defined AI ethics or safety regulations |
|
IoT & Industrial Connectivity |
No specific IoT security mandates for oil infrastructure |
IEC 62443 (Industrial IoT security), ISO/IEC 30141 (IoT Reference Architecture) |
Security risks due to weak IoT regulations |
|
Environmental & Safety Regulations |
National oil & gas environmental laws exist but not digitally integrated |
ISO 14001 (Environmental), OSHA (US Safety Standards) |
Need for digitized compliance tracking & reporting |
|
Digital Contracts & Blockchain |
No legal recognition of blockchain contracts in oil trade |
UNCITRAL Model Law, Smart Contract Standards (Ethereum, Hyperledger) |
Unclear legal framework for blockchain in oil sector |
|
Training & Workforce Compliance |
Limited national policies on digital workforce upskilling |
ISO 29990 (Workforce Learning), IEEE Digital Competency Framework |
Need for government-driven digital skills training initiatives |
Key Observations & Recommendations:
- Iraqi regulations need modernization to align with global best practices, particularly in cybersecurity, data protection, AI governance, and industrial IoT security.
- Strengthening digital compliance frameworks for oil companies is essential to mitigate risks and improve operational efficiency.
- Collaboration with global regulatory bodies (ISO, IEEE, NIST) can help develop standardized digital transformation policies for the Iraqi oil industry.
- Conclusion and Recommendations
- Summary of Key Findings: Digital transformation is crucial for enhancing efficiency, safety, and profitability in the Iraqi oil sector.
- Strategic Recommendations for Iraqi Oil Companies:
- Invest in modernizing IT infrastructure and cybersecurity frameworks.
- Foster a digital culture and upskill the workforce.
- Leverage AI, IoT, and big data analytics for operational improvements.
- Ensure regulatory compliance with national and international standards.
- Establish a long-term digital transformation roadmap with measurable KPIs.
- Call to Action for Industry Leaders and Policymakers: Collaborative efforts between government bodies, oil companies, and technology providers are needed to drive digital transformation successfully.
References
- Accenture. (2021). Digital transformation in the oil and gas industry: Strategies for success. Retrieved from https://www.accenture.com
- Al-Fattah, S. M. (2020). Digitalization in the petroleum industry: Challenges and opportunities. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology, 10(2), 715-725. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13202-020-00865-7
- Deloitte. (2023). 2023 Oil and Gas Digital Trends: Technology and transformation in energy. Retrieved from https://www2.deloitte.com
- International Energy Agency (IEA). (2021). The role of digitalization in energy transitions. Retrieved from https://www.iea.org
- KPMG. (2022). The future of digital transformation in oil and gas: Best practices and strategies. Retrieved from https://home.kpmg.com
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). (2018). Cybersecurity framework for improving critical infrastructure. Retrieved from https://www.nist.gov
- Oil & Gas Journal. (2023). Digital technologies in upstream operations: Enhancing efficiency and sustainability. Oil & Gas Journal, 121(6), 34-41.
- PwC. (2023). The impact of artificial intelligence and IoT in oil and gas operations. Retrieved from https://www.pwc.com
- World Economic Forum (WEF). (2020). The digital transformation of industries: Oil and gas sector insights. Retrieved from https://www.weforum.org
- https://www.undp.org/arab-states/press-releases/turning-point-iraqs-leap-digital-economy
- https://meatechwatch.com/2025/02/18/iraq-launches-digital-transformation-and-automation-center-to-drive-technological-growth
- https://www.agbi.com/banking-finance/2025/02/iraq-plans-digital-currency-to-replace-paper-notes/
- https://www.theguardian.com/business/article/2024/sep/09/bp-ai-deal-palantir-oil-gas-artificial-intelligence
- https://arramton.com/blogs/unleashing-the-potential-of-artificial-intelligence-in-the-oil-and-gas-industry-10-use-cases-benefits-and-examples
- https://www.mrt.com/business/oil/article/survey-finds-energy-finds-struggle-reskill-20221689.php
- https://www.reuters.com/business/energy/official-ceraweek-ai-leading-faster-cheaper-oil-production-executives-say-2025-03-14/
- https://www.appventurez.com/blog/digital-transformation-in-oil-and-gas



